- Understanding Greenhouse Heating Systems
- Cost-Effective Ways to Heat a Greenhouse
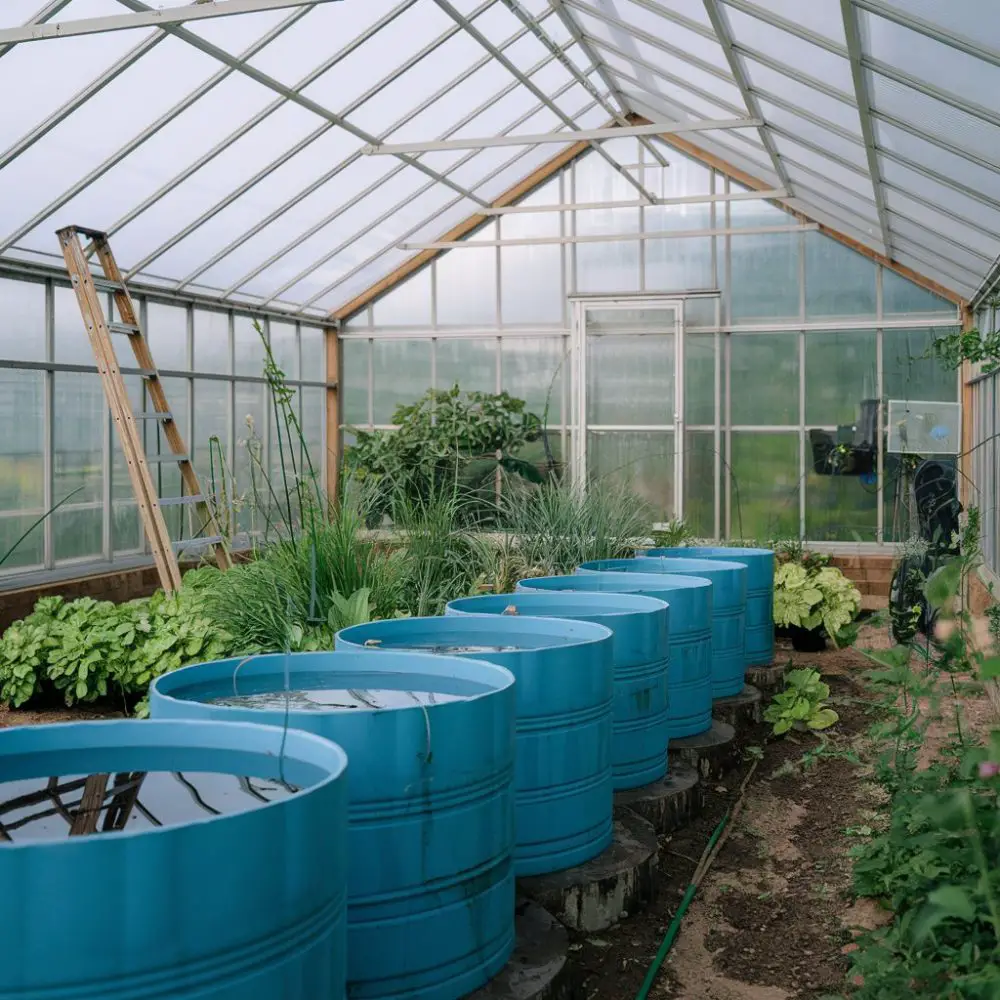
- 1. Utilize Thermal Mass for Heat Retention
- 2. Improve Energy Efficiency
- 3. Ensure Proper Ventilation
- 4. Incorporate Compost Heating
- 5. Know Your Plants’ Temperature Needs
- 6. Choose the Right Heating System
- 7. Employ Cold Frames and Row Covers
- 8. Use an Air Filter
- 9. Monitor Heat Output
- 10. Leverage Geothermal Heating
- 11. Incorporate Supplemental Lighting
- 12. Be Prepared for Emergencies
- Conclusion
How to Keep a Greenhouse Warm in Winter
Greenhouses allow gardeners to enjoy fresh produce year-round, but they can struggle to maintain warmth during colder months. Without proper heating, plants may not survive harsh temperatures. Fortunately, there are several cost-effective ways to keep a greenhouse warm, ranging from passive heating methods to active heating systems.
Understanding Greenhouse Heating Systems
Greenhouse heating systems generally fall into two categories: passive and active.
- Passive Systems: These rely on natural convection currents to circulate warm air inside the greenhouse. They typically involve techniques like thermal mass storage, insulation, and solar heat capture.
- Active Systems: These use mechanical components like fans, heaters, or pumps to distribute warm air. While more efficient, they require an external power source and ongoing maintenance.
Choosing the right heating system depends on your budget, climate, and the temperature requirements of your plants. Additionally, placement of vents and heating units is crucial to avoid issues like carbon monoxide buildup.
Cost-Effective Ways to Heat a Greenhouse
There are several inexpensive yet effective ways to maintain warmth in your greenhouse during winter:
1. Utilize Thermal Mass for Heat Retention
Placing large, water-filled containers inside your greenhouse can absorb heat during the day and release it at night, stabilizing temperatures. Some gardeners use black barrels or even an aquarium heater in a large water storage container to maintain warmth efficiently.
2. Improve Energy Efficiency
To keep heating costs down, consider:
- Insulated greenhouse walls: Bubble wrap, double-layered polyethylene, or polycarbonate panels help retain heat.
- Sealing gaps and drafts: Use weather stripping to eliminate cold air leaks.
- Adding thermal mass: Position black polyethylene sheeting on interior walls to capture and radiate heat.

3. Ensure Proper Ventilation
Proper ventilation prevents condensation, which can lead to mold and plant disease.
- Install insulated vent hoods to retain warm air while still allowing airflow.
- Use exhaust fans or air circulation fans to distribute warm air evenly.
4. Incorporate Compost Heating
Compost piles generate heat as organic materials decompose, making them a natural heat source for your greenhouse. Placing compost bins inside or adjacent to the greenhouse can provide consistent warmth while enriching the soil.

5. Know Your Plants’ Temperature Needs
Different plants require varying temperatures.
- Cold-hardy plants like kale and spinach can survive in lower temperatures.
- Warm-weather crops like tomatoes need extra heating—position heaters near south-facing windows to maximize warmth.
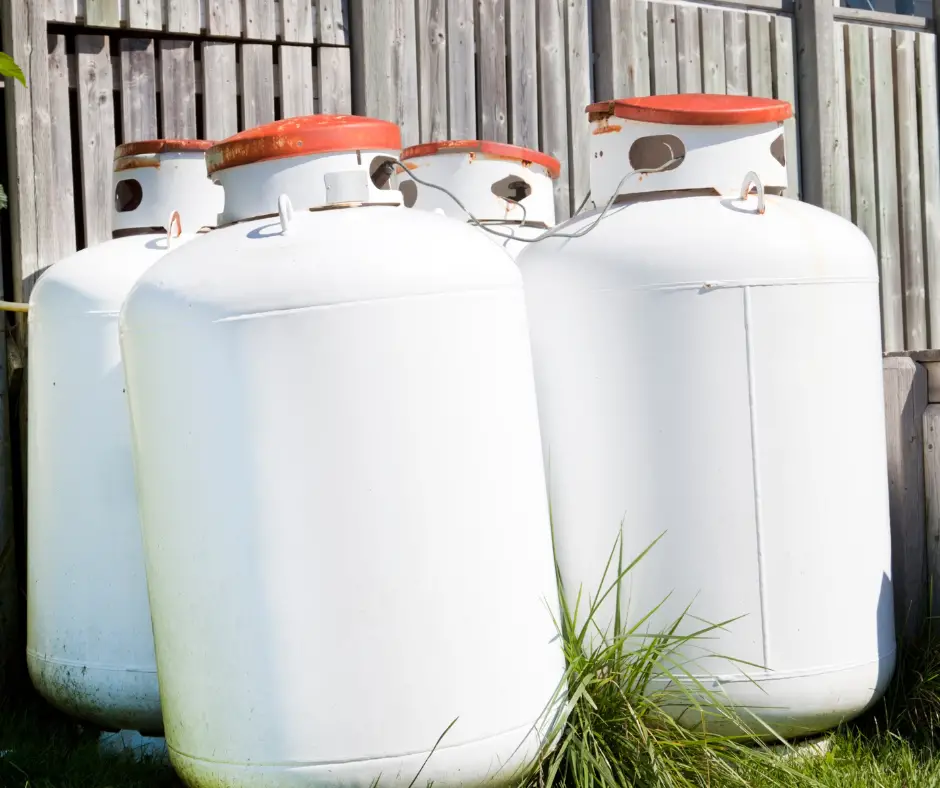
6. Choose the Right Heating System
Greenhouses can be heated using electric or propane heaters.
- Electric heaters require no special wiring and are easy to install. Make sure the unit has an R-value of at least 4 for energy efficiency.
- Propane heaters need proper ventilation to prevent gas buildup. Propane tanks come in various sizes, typically between 8 to 60 gallons, depending on your needs.

7. Employ Cold Frames and Row Covers
Using cold frames or row covers within your greenhouse can add another layer of warmth. These structures create microclimates that protect plants from frost and maintain stable temperatures.
8. Use an Air Filter
Heating systems can collect dust and debris, reducing efficiency. Choose a heater with a built-in air filter to maintain clean air circulation.
9. Monitor Heat Output
Observe air circulation and temperature fluctuations.
- Check how quickly the air warms up after turning on the heater.
- Adjust heater wattage if necessary to avoid overheating or underheating.
10. Leverage Geothermal Heating
If you’re willing to invest in infrastructure, a geothermal heating system can be highly effective. This involves running air through underground pipes, where the earth’s stable temperature helps regulate the greenhouse climate year-round.
11. Incorporate Supplemental Lighting
During winter, shorter daylight hours can affect plant growth.
- Use timed grow lights to extend light exposure.
- Position reflective surfaces to maximize available sunlight.
12. Be Prepared for Emergencies
Unexpected events like power outages, extreme cold snaps, or equipment failures can impact greenhouse conditions. Have a backup heating plan, such as:
- Battery-operated heaters
- Portable propane heaters
- Extra insulation materials like thermal blankets
Conclusion
Keeping a greenhouse warm in winter requires careful planning and the right combination of heating techniques. Whether using passive solar heating, insulation, or an active heating system, ensuring your plants receive the warmth they need will keep your greenhouse thriving all year long. By choosing energy-efficient methods and maintaining proper ventilation, you can create an ideal growing environment without excessive heating costs. Incorporating compost heating, geothermal methods, and supplemental lighting can further enhance greenhouse warmth and stability during colder months.

